Endocrine system
Episode #2 of the course “How the human body works”
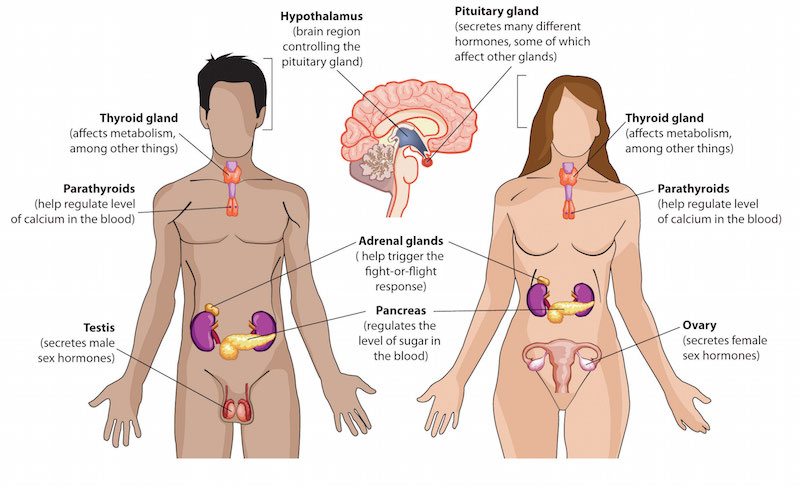
The endocrine system is a series of ductless glands throughout the body that transmit information from one organ to another using chemicals commonly referred to as “hormones.” Most organs in the body release their own hormones, which transfer information and instructions to other organs, and the endocrine system is responsible for relaying these messages. Its main switchboard is the hypothalamus—a walnut-sized section of the brain—but it also includes the thyroid, pituitary gland, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
“Endo” means “inside,” as opposed to “exo,” which means “outside.” All endocrine system hormones are meant to function inside the body (unlike sweat, for example, which is an exocrine product). Hormones can be secreted into the circulatory system, where they will be carried to other organs to perform their function, or they can be secreted directly from one organ or part of an organ onto another if the organs are touching.
The most common and interesting hormones serve multiple purposes, with different effects on different organs. For example, when the adrenal glands secrete adrenaline (or “epinephrine”), the hormone causes blood to flow because the heart beats faster. This slows digestion, but it heightens skeleto-muscular function—it causes high blood pressure but also an increased alertness. Adrenaline is responsible for the “fight or flight” response triggered during fear. Other hormones can have multiple effects as well. For example, the hormone testosterone influences muscle development, hair growth, and weight gain, in addition to its effects on the reproductive system.
When one part of the endocrine system does not function properly, it can cause a chain reaction throughout the body by throwing off other chemical reactions. Luckily, medicine has developed chemical controls to manage malfunctioning systems or to manipulate systems to function differently. There are now hundreds of medications available that work off our understanding of hormones—everything from birth control methods to anti-seizure medications to pills that can help you sleep.
Share with friends